One query we get requested not less than one time every week is whether or not or twin socket motherboards meant for twin processors can work with one CPU. A standard driver behind this query is as a result of twin processor motherboards enable for straightforward enlargement at a later date. Add a second CPU, heatsink/ fan and extra reminiscence to a system with out changing any inner elements or including a second machine. The reply to the query “Can I take advantage of one CPU in a twin processor motherboard?” is sure… with some caveats. Let’s discover why.
The overwhelming majority of motherboards “simply work” if you happen to set up a CPU into the bottom numbered CPU slot. That is often CPU0 if there may be CPU0 and CPU1 or CPU1 if the board is tagged CPU1 and CPU2. That is true for each Intel and AMD motherboards basically and when unsure, most motherboard manuals will instruct a consumer as to which processor slot may be populated by a single CPU and a twin CPU motherboard. Right here is an instance from a Supermicro X8DTN motherboard that was a reasonably well-liked twin processor Intel 5500 and 5600 collection Xeon motherboard.
Because the Intel 5500 and 5520 collection chipset had an IOH northbridge, populating just one CPU slot within the twin socket motherboard didn’t lower out any extra motherboard assets. Within the Intel socket LGA1366 days, and with the AMD C32 and G34 platforms, each the northbridge and southbridge had been discovered on the motherboard so the CPUs usually related by the northbridge to get to an enlargement card bus. In these programs, the primary impression of solely having one CPU (apart from the apparent loss in CPU efficiency with out the second CPU) is that one couldn’t populate the reminiscence banks for the empty processor slot. That is similar to the only CPU nodes we use for the STH colocation undertaking, despite the fact that every Dell C6100 node is twin processor succesful.
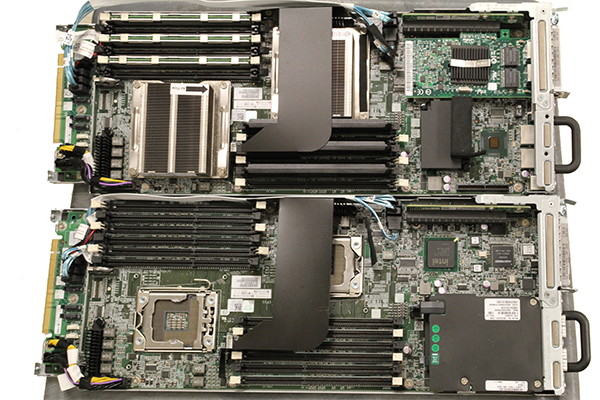

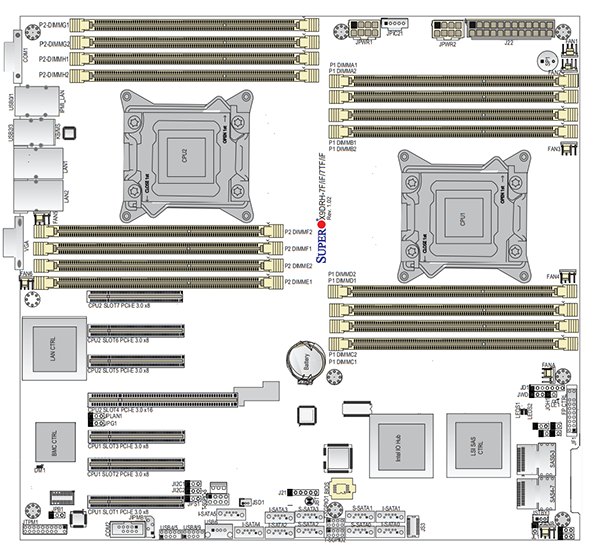
Beneath these heatsinks on the higher node sits just one processor regardless of the board being dual-processor succesful. One may also see that the related DRAM financial institution is stuffed with DDR3 RDIMMs whereas the empty socket is using DIMM blanks. This setup is way totally different than a extra fashionable LGA2011 twin Intel Xeon motherboard. Right here is an instance of a Supermicro X9DRH-7TF which has each onboard LSI SAS and Intel X540 10GbE:

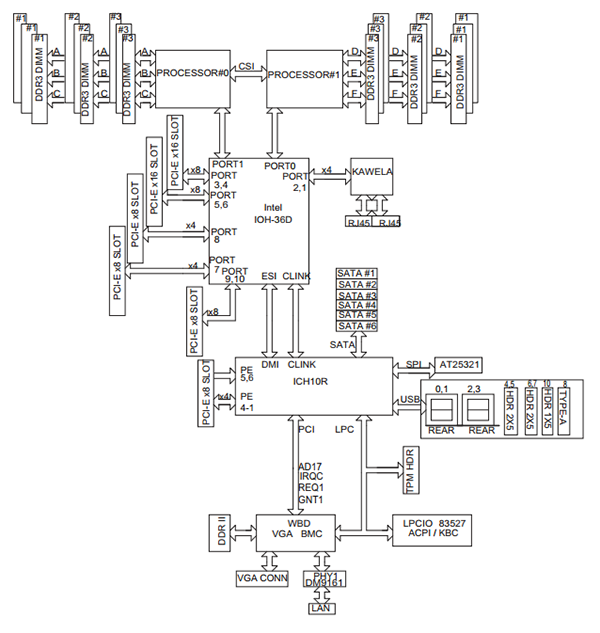
Right now’s architectures add one other stage of complexity. With the twin Intel Xeon E5 LGA2011 platform for example, the PCIe enlargement slots are straight tied to a CPU. On the image above, one can see every PCIe slot tied to a selected CPU. When a CPU socket will not be populated, the PCIe lanes don’t terminate. This has a significant impression on the performance of the motherboard. For instance, if the second CPU socket will not be stuffed in a twin socket motherboard oftentimes onboard gadgets corresponding to Ethernet and SAS controllers could not work. Moreover, PCIe lanes could not work. It will render the slots ineffective till the extra CPU(s) are added. Right here is an related diagram for the Supermicro X9DRH-7TF:

Right here we are able to see that if CPU1 was lacking, the onboard Intel X540 10GbE LAN and LSI SAS2208 controller shouldn’t have a PCIe however to hold off of. Conversely, with no CPU2, one wouldn’t have entry to a number of PCIe 3.0 x8 slots. Fortunately, most motherboard producers state of their manuals which socket to populate.
Any additional questions be happy to ask within the boards!
