So you’ve got yourself one of the best AMD Ryzen CPUs and want to squeeze some extra performance out of it. Thankfully, AMD’s own free utility called Ryzen Master makes CPU overclocking extremely simple. If you have a Ryzen 2000 series or newer desktop processor, you can safely overclock your CPU using Ryzen Master in the regular Windows environment. There’s no need to head into your BIOS.
Ryzen Master not only allows you to overclock your CPU but also your memory and integrated Radeon graphics. You can also undervolt your CPU if that’s something you prefer. And you can even save overclocking profiles and monitor your CPU temperature, voltage, power, and more. Ryzen Master is meant to simplify overclocking for AMD’s unlocked Ryzen processors and enables users to make the most of their AMD CPUs. This guide will give you a basic overview of everything you can do with Ryzen Master and how to use its various features.
Before you overclock: Points to remember
Overclocking involves tweaking your CPU’s stock frequency and/or voltage to boost performance. It involves careful trial and error so that you don’t end up damaging your CPU. It’s always recommended to keep the following points in mind before you go about overclocking your processor:
1. Get a decent CPU cooler
Overclocking will invariably send more power to your chip and raise temperatures. If you don’t have sufficient cooling for your CPU, things could get messy. It’s rare to damage your CPU with minor overclocking, but you’ll still end up with unstable overclocks and BSODs. If you don’t have one already, try to get one of the best AMD AM5 coolers to keep CPU temps in check. These coolers will work fine even with your AM4 motherboard. While you’re at it, ensure you have some intake fans and exhaust fans in your case as well. Our list of the best PC case fans could help you pick some.
2. Follow the precautions
Whenever you’re running your processor at settings other than its factory settings, you do run the risk of voiding your warranty in case something bad happens. But, as long as you follow all the precautions and don’t apply random OC settings you got off the internet (even if it’s for your exact CPU model), you’re going to be fine. Due to the “silicon lottery” — meaning manufacturing variations — no two chips of the same processor model have the same overclocking headroom. You need to find the settings that work for your specific chip through trial and error.
3. Benchmark your PC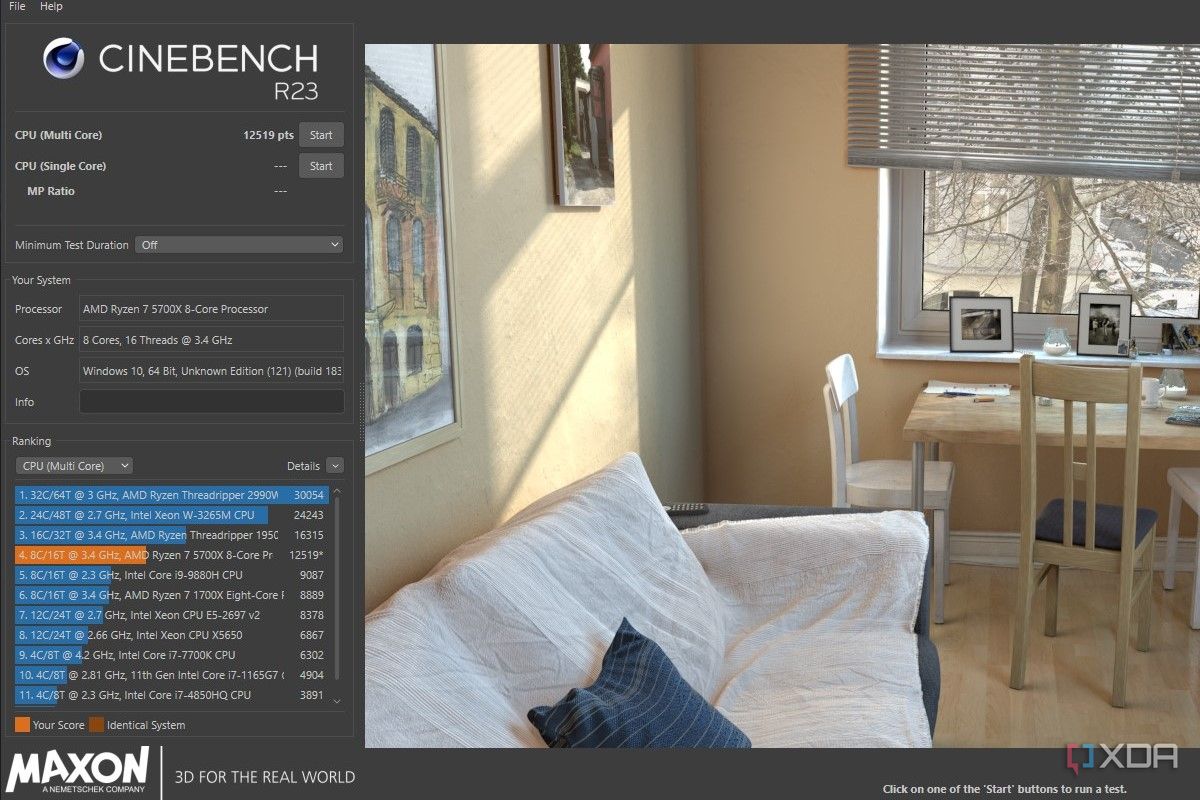
It’s important to benchmark your PC at stock settings before you do any overclocking. After all, you need something to compare to afterward to see if your overclock produced any significant performance boost or not. Use Cinebench R23 to run some single-core and multi-core tests and note down the average scores for each test. These will come in handy later when you run the post-OC Cinebench tests.
Overclocking Ryzen CPUs with Ryzen Master
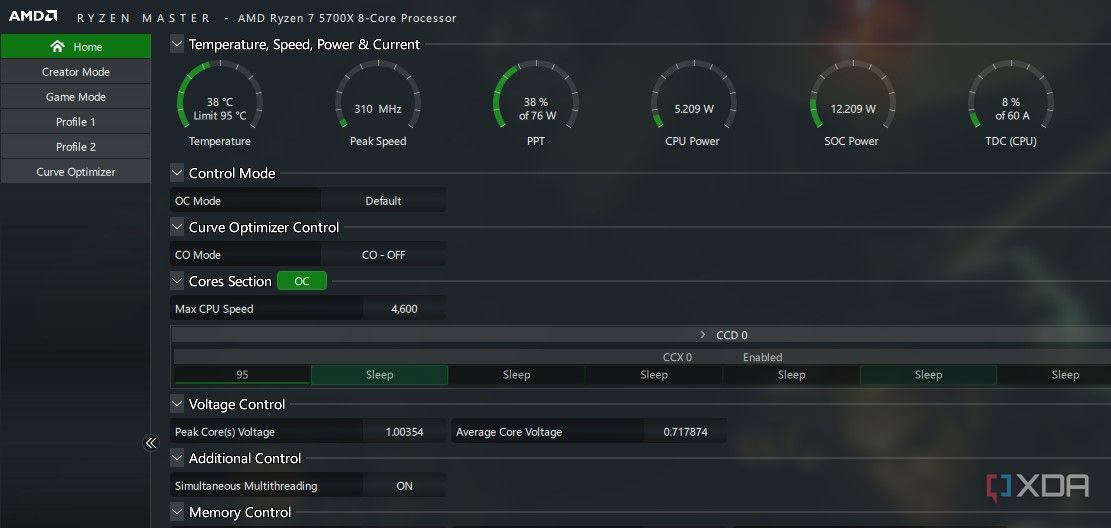
When you launch Ryzen Master and accept the warning message, you’ll be greeted with the Home screen. This screen shows you sections like Temperature, Speed, Power & Current for system monitoring, including Control Mode, Curve Optimizerand Cores Section options for any existing overclock details, as well as Voltage Control, Additional Controland Memory Control for deeper overclocking information. If you don’t see this screen on launch, you’re likely in the Basic View. Simply click Advanced View to change views.
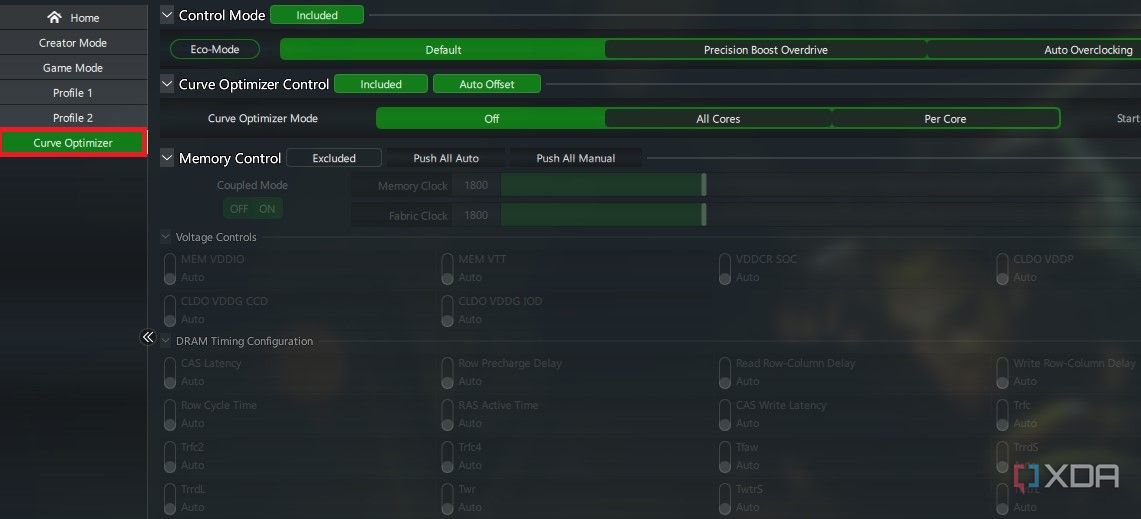
This screen is only for you to monitor your CPU readings. For the actual overclocking process, you’ll need to use one of the sections on the left, just below the Home tab. The Creator Mode and Game Mode are pre-configured profiles that we’ll not get into for the purposes of this guide. Just know that for 8+ core CPUs, Game Mode limits them to using only 8 cores. We’ll use Profile 1 to show the various overclocking modes you can use. Profile 2 is simply an additional profile and the Curve Optimizer section enables you to undervolt your processor to allow for a cooler operation. We’ll cover all these sections in detail below.
Overclocking with Precision Boost Overdrive mode
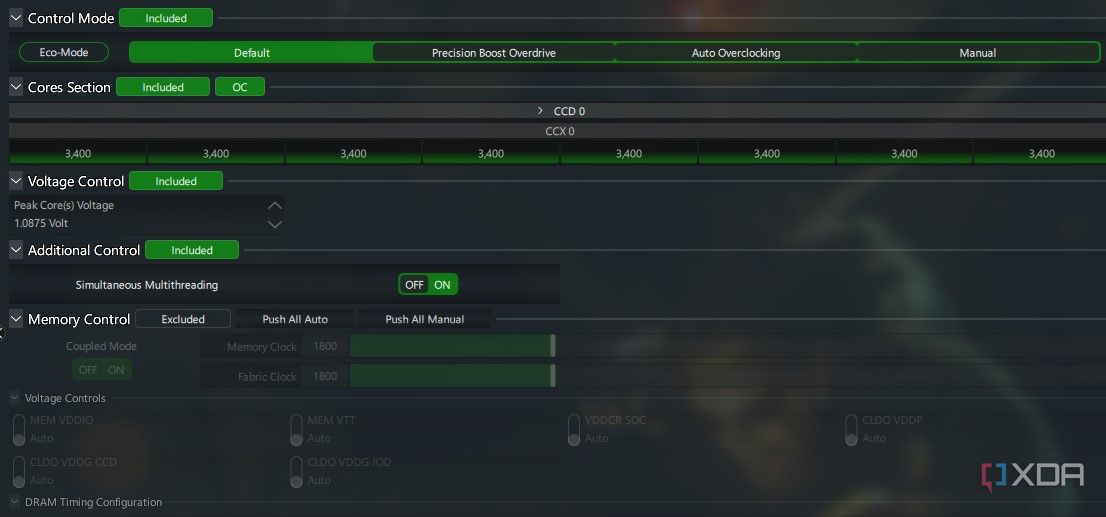
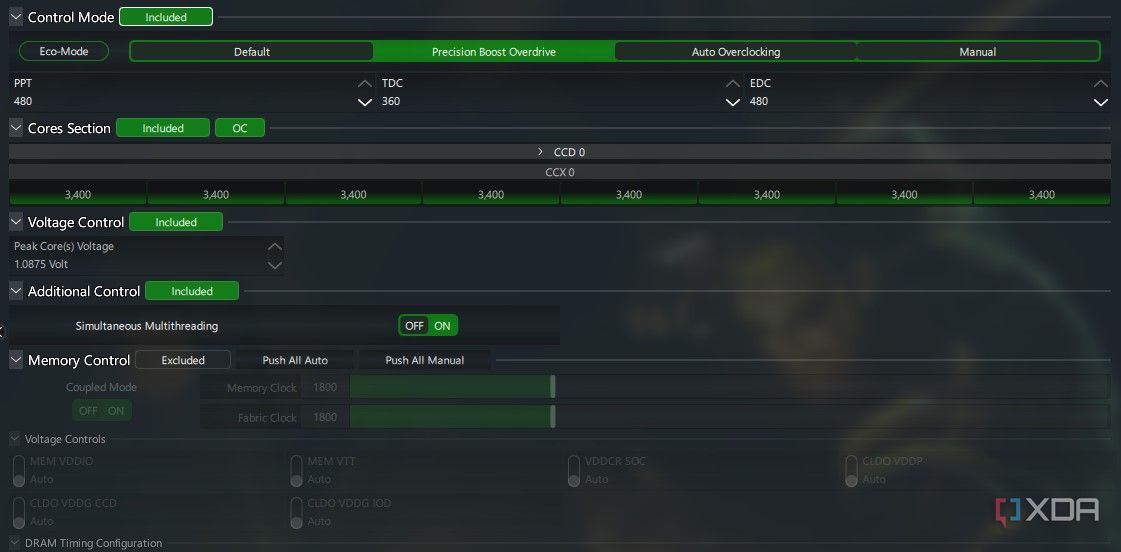
Once you’ve clicked Profile 1you’ll be able to see options called Default, Precision Boost Overdrive, Auto Overclockingand Manual at the top, under Control Mode. We’ll begin with Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO) and then cover the other options in the following sections.
PBO is a mechanism by which your CPU attempts to achieve your CPU’s advertised boost frequency more often and for longer. It does this by changing its power and current settings denoted by the PPT (Package Power Tracking), TDC (Thermal Design Current), and EDC (Electrical Design Current) limits. It’s an automatic process that uses the existing, automated boost mechanisms of your CPU and motherboard to improve multi-threaded workload performance. The voltage settings are not user-modifiable in the PBO mode, but they’ll still get tweaked by the utility. You can leave Additional Control and Memory Control unchanged and simply click Apply at the bottom of the window to activate the overclock.
The other settings besides Apply can be used to discard changes, save or reset profiles to default settings, or copy the current settings. The PBO overclock doesn’t need a system restart so you can move on to running a Cinebench R23 multi-thread test and compare the performance against the stock benchmark.
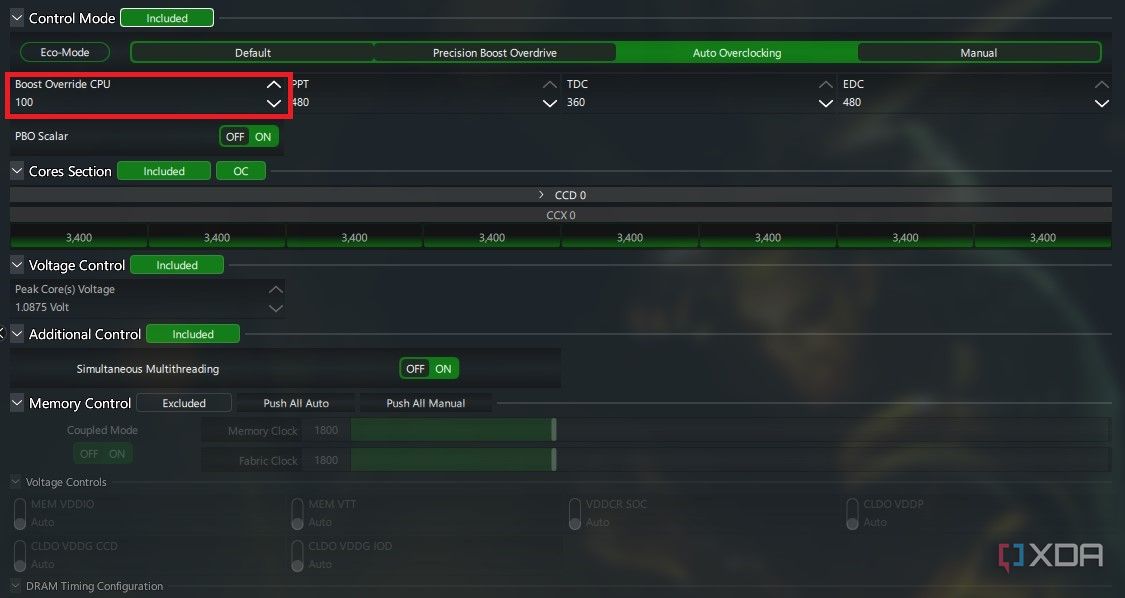
Overclocking with Auto Overclocking mode
The Auto Overclocking section allows your CPU to exceed even the advertised boost clocks, although still limited by the CPU’s automated boost mechanisms. It’s a more aggressive overclock as compared to PBO, as it can automatically manipulate the CPU settings to achieve the CPU frequency you want. Voltage control is again locked but you can use the Boost Override CPU to enter the CPU frequency you want in a step fashion. It’s best to increase this value in increments of 25 or 50 and then test the stability of the overclock with Cinebench R23. If the test hangs or crashes the system, reboot and try a lower frequency. You’ll be able to achieve a stable frequency limit for your CPU in a few tries.
If you have integrated Radeon graphics on your processor, it will also show up under APU GFX Speedsright below Additional Control. By default, the auto OC settings will overclock your Radeon graphics as well. You can leave settings like PBO Scalar, Additional Controland Memory Control untouched for now. Remember that the Auto OC mode requires a system restart whenever you apply new settings.
Overclocking with Manual mode
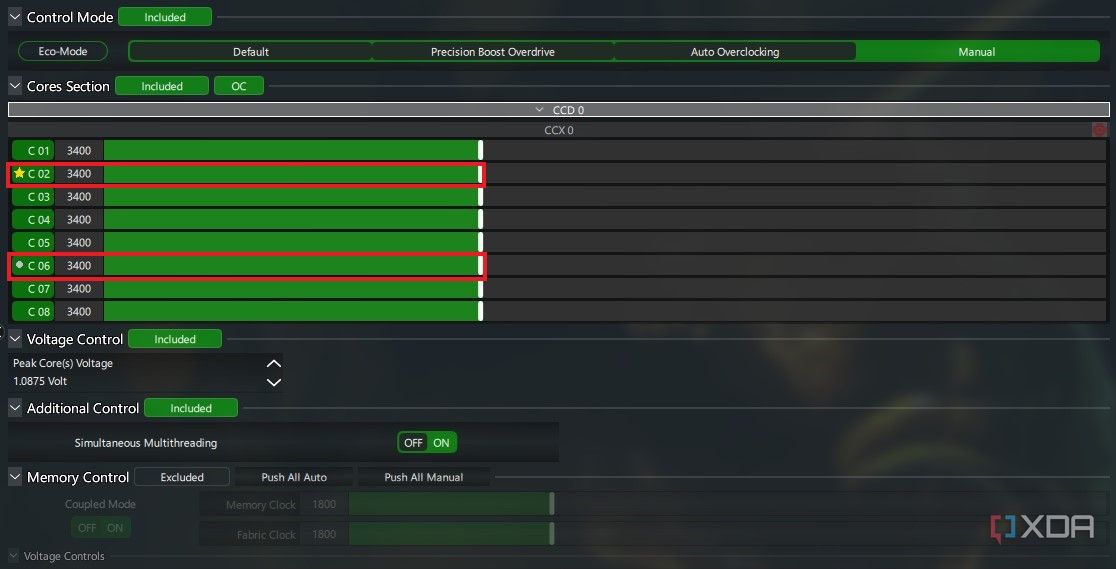
Finally, using the Manual mode can unlock even higher frequencies for your CPU as compared to the Auto Overclocking mode. This mode not only allows you to set frequency increments on a per-core basis but also fully unlocks Voltage Control so you’re no longer limited to your CPU’s automated boost mechanisms. You can expand the CCX sections to see the individual core frequencies of your CPU. Depending on your model, you can see one or two CCX and CCD sections. Once expanded, the CCX section denotes the core with the most overclocking potential with a yellow star and the second-most overclockable core with a gray circle.
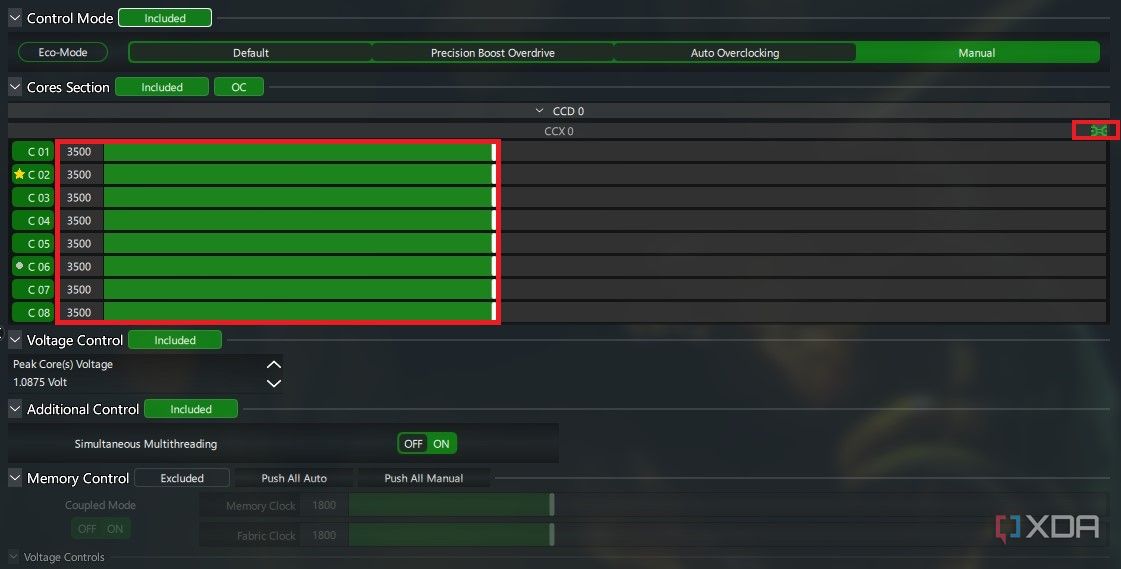
Move the slider next to the core denoted by the yellow star if you want to overclock only the fastest core. Otherwise, if you want to run a simpler all-core overclock, you can click the small red-colored button at the end of the CCX row to turn it green. Then, move any of the sliders to apply the same frequency boost to all the cores simultaneously. You can also need to increase the voltage in small increments and test the overclock after each increase. If Cinebench hangs or crashes, you might need more voltage to sustain the frequency. Keep an eye on the CPU temperature just before the crash. If it’s very high, you might need to lower the frequency instead to achieve a stable overclock.
Ryzen Master doesn’t restart the system when applying a Manual overclock but it will prompt a restart when changing modes from Manual to something else.
Undervolting Ryzen CPUs with Ryzen Master
Overclocking is not the only thing you can do with Ryzen Master. In some scenarios, undervolting your Ryzen CPU might be a better option. Maybe you don’t need any extra performance from your CPU and simply need lower temperatures without any hit to stock performance. This is exactly what the Curve Optimizer section can achieve by automatically manipulating the voltage-frequency curve of your CPU. Note that this feature is only available for Ryzen 5000 and Ryzen 7000 series processors.
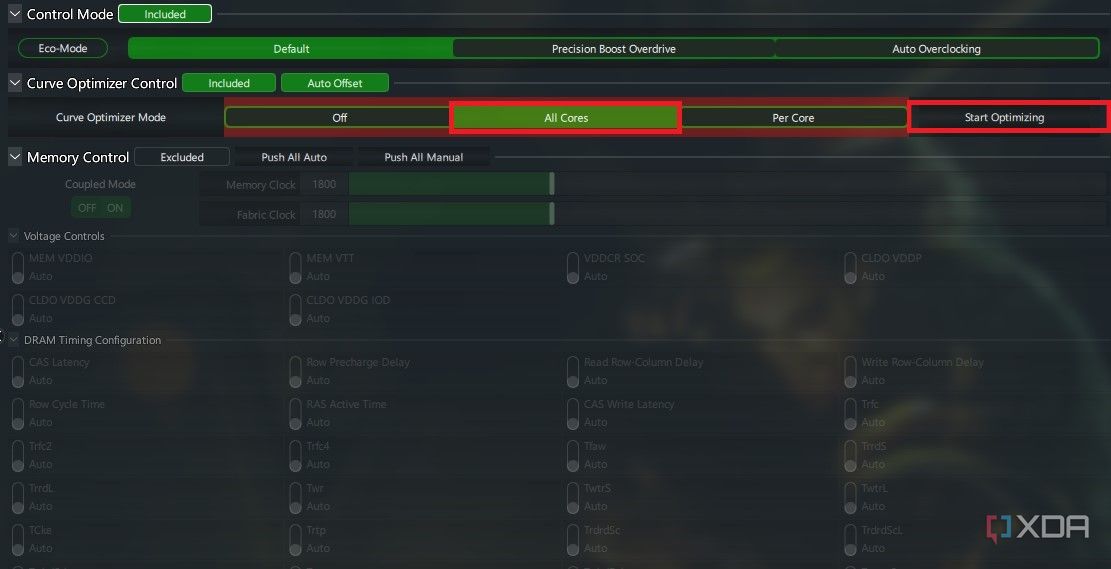
Once you’re in the Curve Optimizer section, keep things simple and select All Cores next to Curve Optimizer Mode. Click Start Optimizing to get the best settings for your CPU displayed under a new section called CO All Core Valuejust under Curve Optimizer Mode. This optimization process can take some time and could restart your system as well. Once the settings are displayed, you can click Apply to run the Curve Optimizer. You can monitor your CPU temps and compare them to stock settings to see if the undervolt really reaped some benefits.
You might have noticed Eco-Mode next to the various overclocking modes. If you’re looking to run your CPU in a low-powered state for a while, you can use this mode. It’s a simplified way to get lower CPU temps when you don’t even need stock performance.
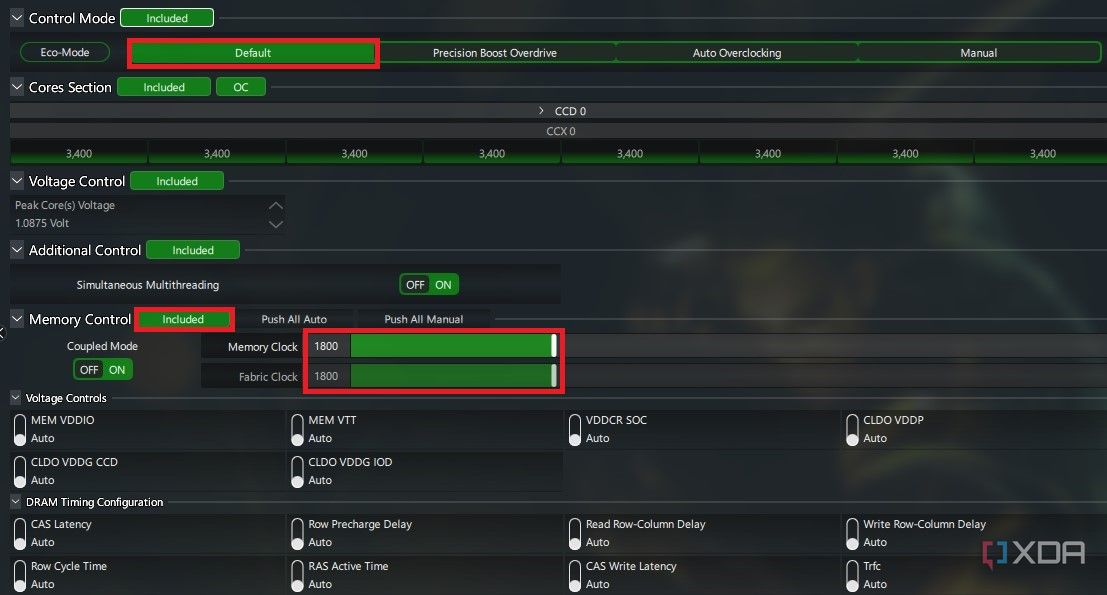
Overclocking RAM with Ryzen Master
Memory overclocking is also possible with Ryzen Master. The Memory Control section you’ve been seeing till now is used to overclock your RAM to yield some more performance benefits. Memory overclocking can be beneficial in older, low-powered systems or in cases when you want to run your high-end RAM at the maximum possible settings.
For memory overclocking, you simply need to select the Default mode under any profile and switch Memory Control to Included. Then, for a simple and stable overclock, leave all settings unchanged and only use the Memory Clock slider to set the frequency to what you want. You can choose half of your memory’s rated speed here or increase it slightly. Apply the changes and run benchmarks to test the stability of the overclocks.
Other options in Ryzen Master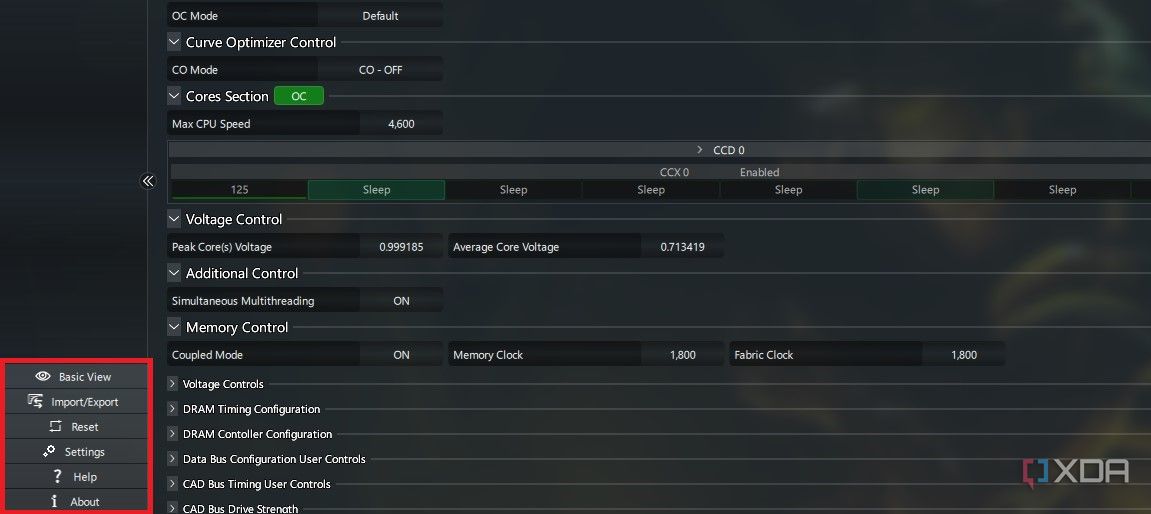
On the bottom-left side of the Ryzen Master window, you’ll notice a few more options. These are basic UI sections that can help you navigate around the program. Basic Vie can help you switch to a more simple view to monitor CPU readings or run quick, one-click overclocks. Import/Export can be used when you want to download your settings to a file or restore them from a file. Reset simply resets all CPU parameters to the default values and Settings takes you to Ryzen Master’s settings screen if you want to change its behavior.
Easy BIOS-free overclocking with Ryzen Master
Ryzen Master makes life simple for AMD Ryzen CPU owners to overclock their processors without needing to go into their BIOS. Although BIOS overclocks are known to be more seamless and generally free from software bugs, Ryzen Master is still the better choice for the average user. If you’re someone who doesn’t want to run a 24×7 overclock, you might not prefer overclocking from the BIOS. You can simply turn overclocks on and off with one click using Ryzen Master.
If you’re on Team Blue, you can safely overclock your CPU with Intel’s Extreme Tuning Utility. And if you want to ensure your motherboard is up to the task, you can consider one of the best motherboards for overclocking for your next upgrade.