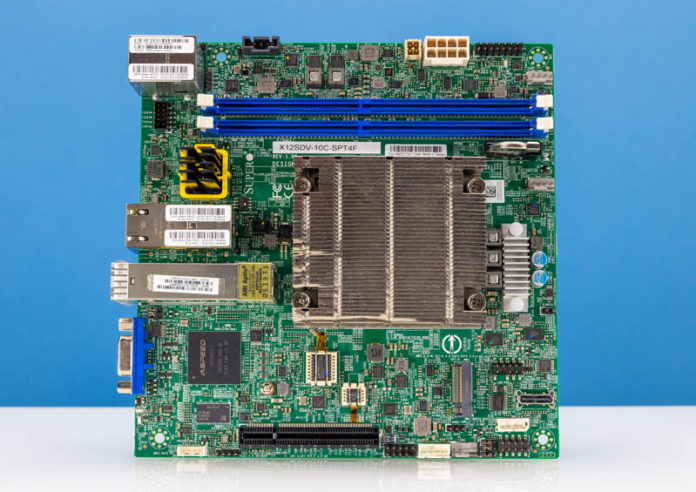

The Supermicro X12SDV-10C-SPT4F is an enchanting platform. It presents strong 10-core Intel Xeon D-1749NT efficiency and different options. For instance, this platform has each 25GbE SFP28 and 10Gbase-T onboard all in a mITX kind issue. We’re going to check out these on this overview.
Whereas we just lately reviewed the Supermicro X12SDV-4C-SP6F, that was a Flex ATX platform. On the finish of the day, many chassis are designed for mITX in order that kind issue distinction can matter, however we’ll be aware that Supemicro additionally has a X12SDV-10C-SP6F in the event you would favor that kind issue and networking mixture.
Supermicro X12SDV-10C-SPT4F Overview
The motherboard itself is certainly one of Supermicro’s mATX edge choices. Whereas Supermicro nonetheless has many mITX choices, the extra capabilities of immediately’s Intel Xeon D traces make the shape issue tougher as we’ll see.
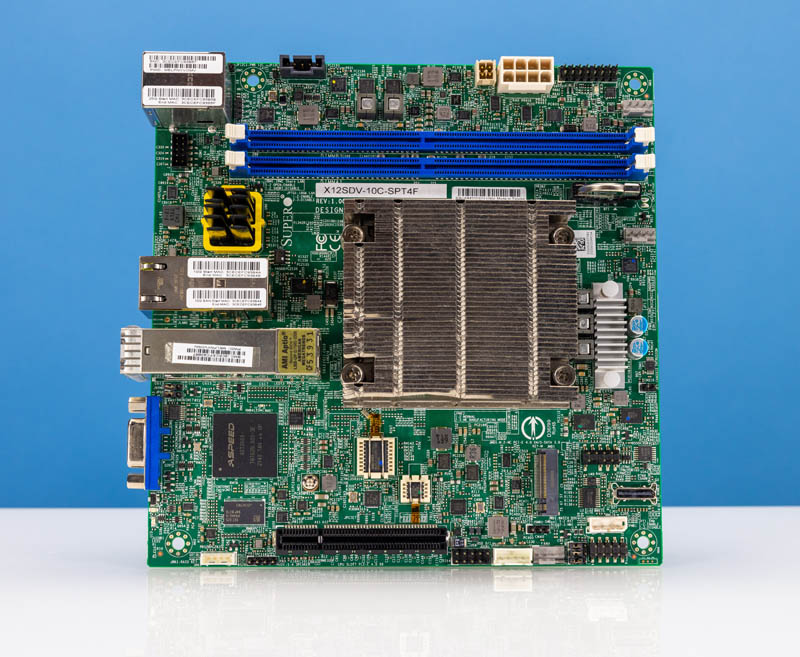

The X12SDV tells us it’s a X12 single-socket Xeon D platform. The -10C- within the mannequin quantity tells us it is a 10-core Xeon D. On this case, it’s the Intel Xeon D-1749NT. If you wish to be taught extra concerning the Xeon D-1700 and D-2700 sequence, take a look at our video:
The half is 10 cores/ 20 threads and has the newer options of the Ice Lake-D era, together with an up to date microarchitecture and PCIe Gen4.
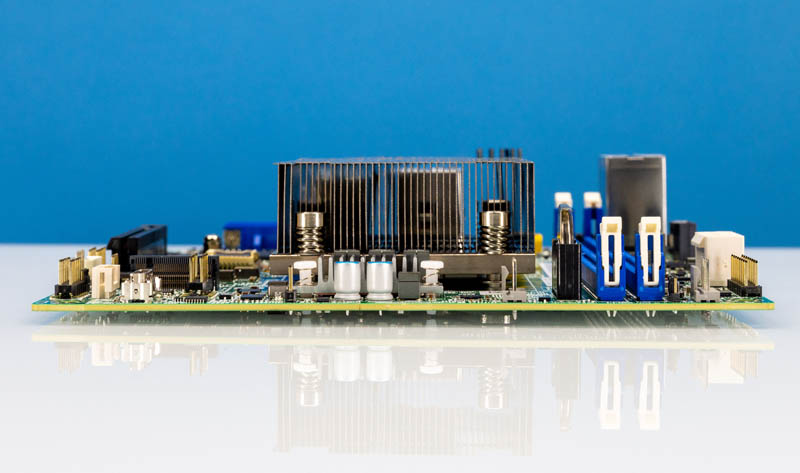
We wished to shortly level out that lots of our readers will see a passive heatsink affixed to this motherboard. That’s as a result of it’s designed for chassis followers offering airflow. The small heatsink shouldn’t be sufficient to maintain the 90W SoC cool with out chassis airflow. 90W is much more than we noticed with the Xeon D-1500 sequence, however idle energy consumption remains to be simply 25-35W relying on the OS and configuration.
Supermicro is utilizing a two-channel and one DIMM per channel (1DPC) structure right here. As we coated in our Welcome to the Intel Ice Lake D Period piece, the Xeon D-1700 truly has three reminiscence channels accessible, however we generally see two channels being positioned as they’re right here.
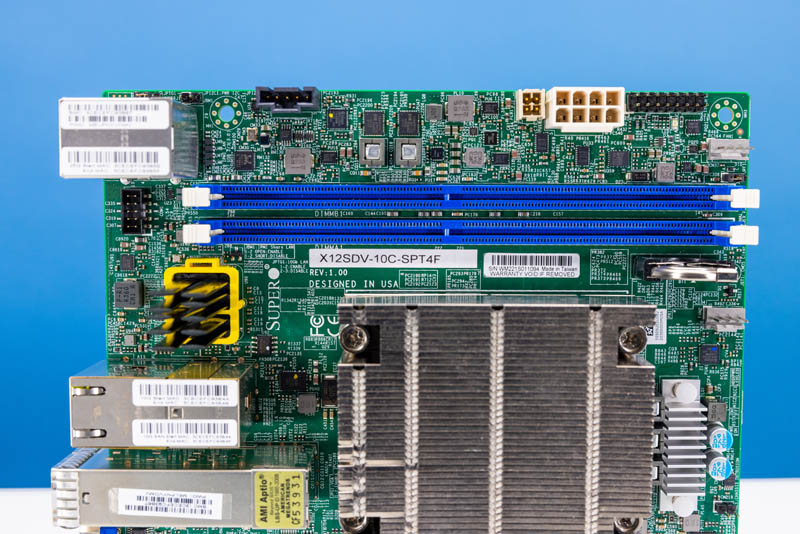
The facility enter right here is targeted on DC energy functions, so we don’t get a normal 24-pin ATX connector. This has been widespread on Supermicro embedded motherboards for a number of generations.
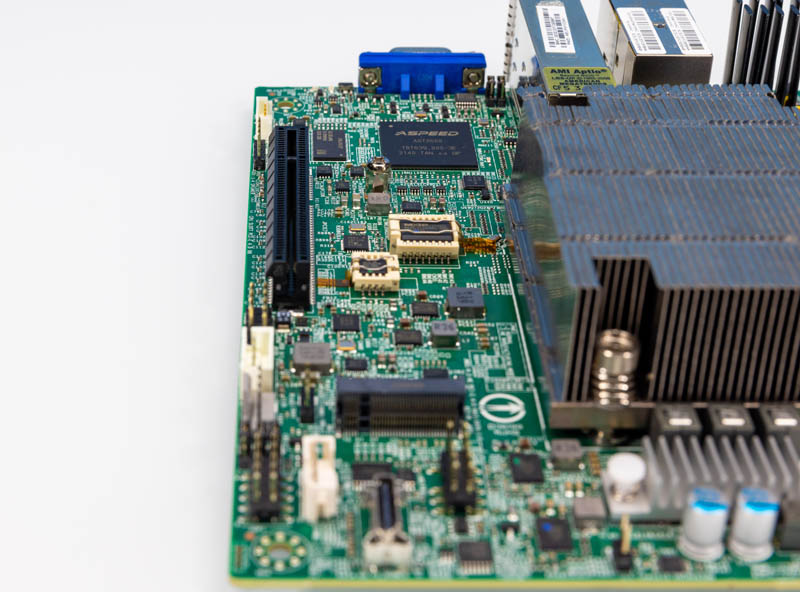
On the underside of the motherboard, we get the BMC, a PCIe slot, a M.2 slot, and an Oculink port.
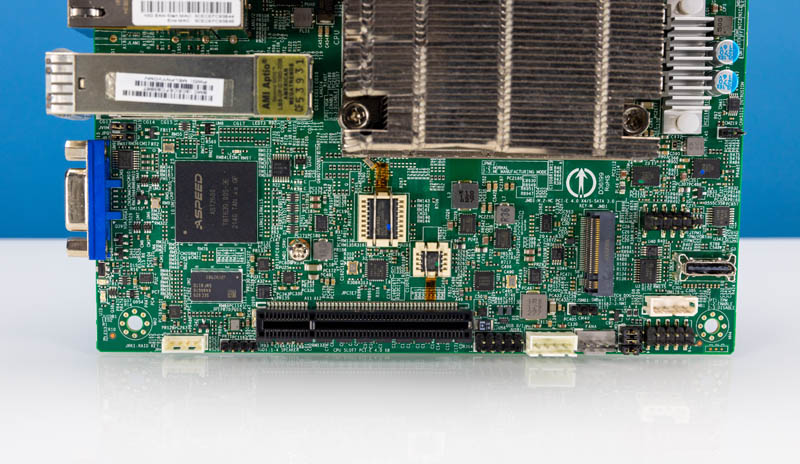

The M.2 slot is each PCIe Gen4 x4 and likewise has a SATA choice.
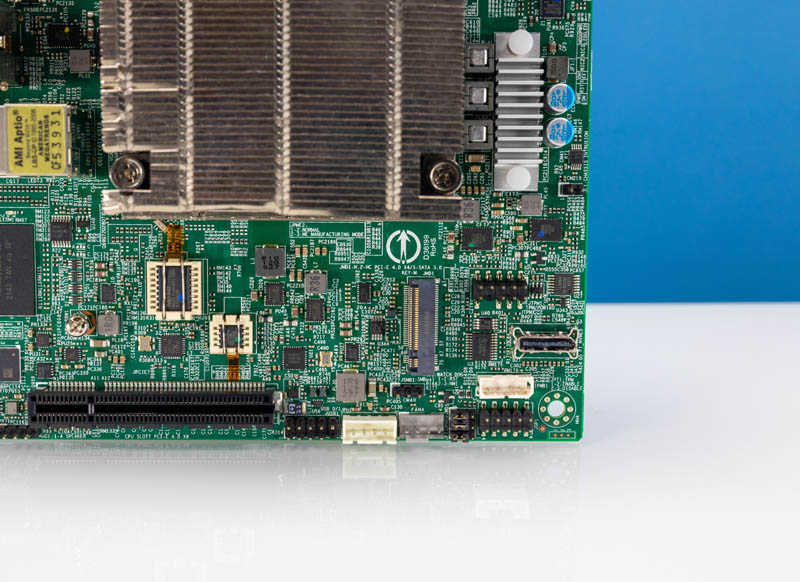

The Oculink port supplies both 4 lanes of SATA III or can present a PCIe Gen3 x4 hyperlink.
The PCIe slot is a PCIe Gen4 x8 slot. One function we recognize is that Supermicro makes use of an open-ended x8 bodily slot permitting for longer playing cards to be positioned within the slot.

A tall heatsink covers the Intel X550 for the rear 10Gbase-T ports. There’s a yellow retention clip round it. The heatsink fins in our check unit received bent throughout delivery, however they nonetheless labored.
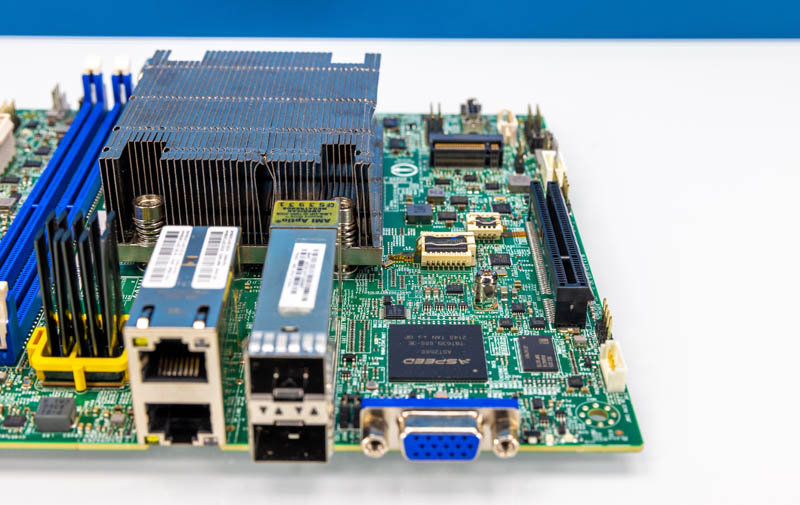
One thing lacking from this era is a standard 7-pin SATA port. There’s merely not one on the motherboard, and there are not any “gold” ports for SATA DOMs. The market has moved to M.2, however it is a pretty notable instance of the place the legacy port has been omitted.
Maybe probably the most thrilling function is the rear I/O. Right here we get Supermicro’s customary two USB 3 Kind-A ports, a VGA port, and an out-of-band administration port. Then comes the networking. There are two 10Gbase-T ports by way of the Intel X550.
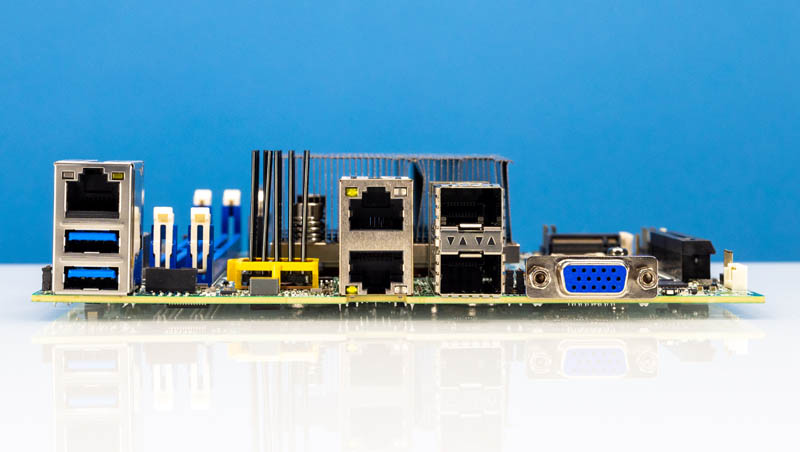
Two SFP28 cages present 25GbE ports that the Intel Xeon D-1700 SoC powers. We’re going to take a look at them in additional depth later on this overview.
Subsequent, allow us to get to administration and efficiency.
